Describe the Receptors for Dynamic and Static Equilibrium
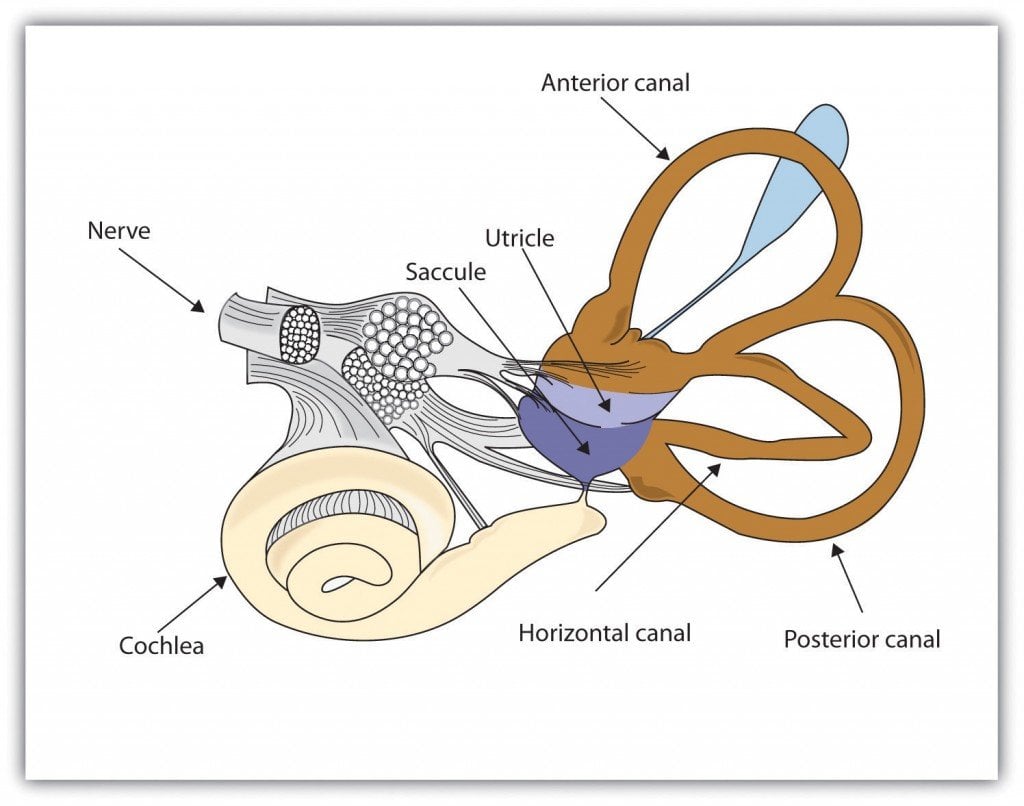
In the inner ear the hearing receptors are stimulated by vibrations in fluids. A sensory receptor called a macula is located in the walls of the saccule and utricle the two bulblike sacs of the vestibule.

Module 12 Special Senses Flashcards Quizlet
Static Equilibrium is the balance maintained by the sensory organs in response to movements of the body mainly the head relative to the forces of gravity acceleration deceleration.
. Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Describe the organs of static and dynamic equilibrium and their functions -Static Equilibrium maintains the stability of the head and body when they are motionless. Dynamic equilibrium - a special sense in which interprets balance when one is moving or at least to the head is moving.
The vestibular system consists of two bulblike sacs the saccule and the utricle - both of which contain a sensory receptor in their walls called the macula. In physics equilibrium refers to the state of any object when all forces acting upon it result in zero change of motion for the object. What is the range of sound frequencies that humans can hear.
-The receptors for dynamic equilibrium are called maculae. In the case of a static equilibrium as in a dynamic equilibrium the number of reactants and the number of products remain the same. Auditory receptors are located in the cochlea.
Hair cells in the maculae of the utricle and saccule bend are used to detect changes that help maintain static equilibrium. Static equilibrium indicates that the object in question is motionless. Experts are waiting 247 to provide step-by-step solutions in as fast as 30 minutes.
Outer ear contains ear pinna for sound signals collection. Dynamic equilibrium indicates that the object is moving and will continue to do so unchanged. 15 What do the receptor cells for hearing static equilibrium and dynamic equilibrium have in common- All receptor cells are transducers.
There are two types of equilibrium. Receptors are proteins that bind to specific or non-specific. 16 Would the receptors for equilibrium work in space at zero gravity- They wouldnt work very well because the receptors in the ear depend on gravity.
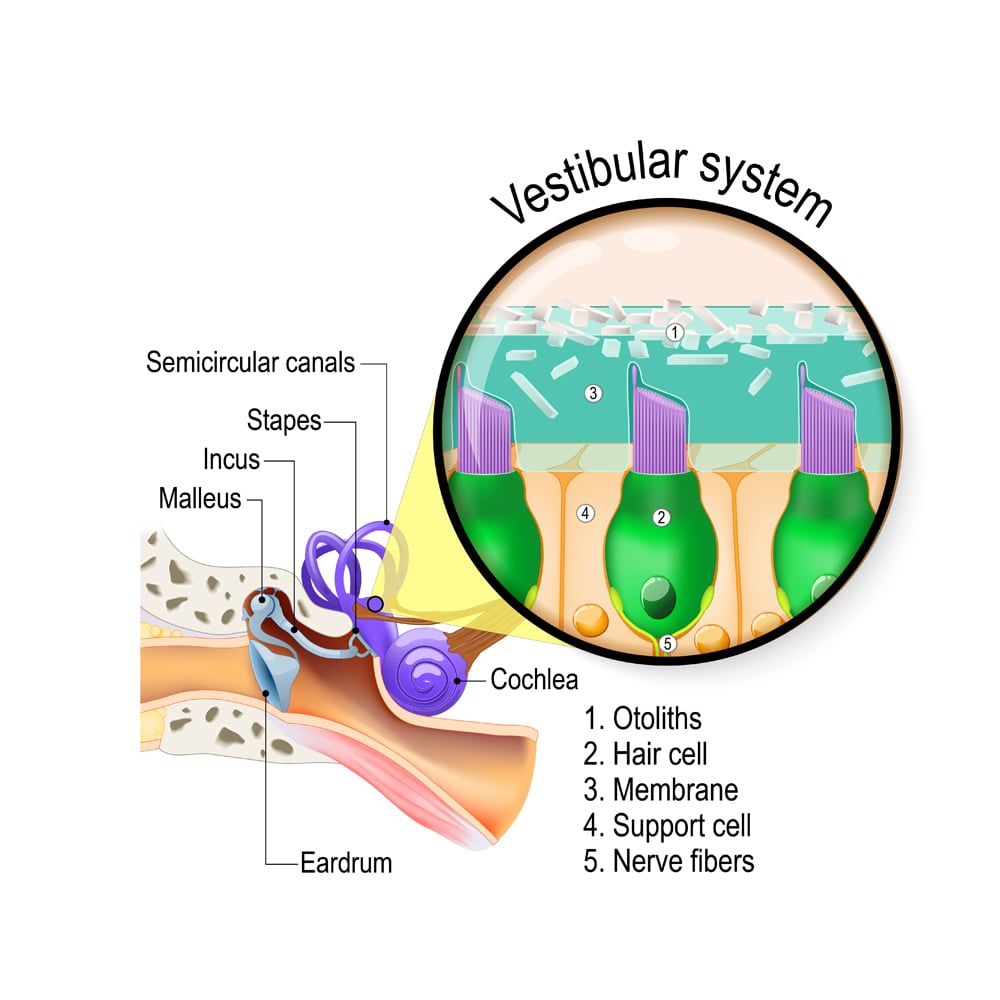
The vestibule is responsible for maintaining static equilibrium while the semicircular canals maintain dynamic equilibrium. Static gravitational equilibrium which involves the movement of the head with respect to gravity and dynamic rotational equilibrium which involves acceleration of the head in rotation horizontal and vertical movements. Dynamic receptors located in the semicircular canals crista ampullaris have embedded in the gel-like cupula.
The receptors for static equilibrium are found in the maculae of the saccule and utricle. However the reactions itself has come to a halt without any more reactants converting into products and vice versa. What is the meaning of the term blind spot in relation to the.
Responds to straight line movements. The saccule utricle and three semicircular canals together form vestibular apparatus which is responsible for the static and dynamic equilibrium. The semicircular Canals contain the receptors for dynamic equilibrium.
There are five vestibular structures each containing a specialized mechanoreceptor a maculae within the utricle and. Similar to the cochlea the both the vestibule and semicircular canals use hair cells with stereocilia to detect movement of. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Define and describe the structure location and innervationpathway of gustatory receptors. Receptors within the membrane sacs of the vestibule that are essential to our sense of static equilibrium. The functional components of the membranous labyrinth involved in the sensations of static and dynamic equilibrium are a system of thin-walled intercommunicating tubes and ducts situated within the petrous part of the temporal bone at the base of the skull.
Static equilibrium - equilibrium of the system whose parts are relatively at rest such as a steel truss resting on Piers. Inner part of ear contains vestibule that regulates static equilibrium and semicircular canals that regulates dynamic equilibrium. This problem has been solved.
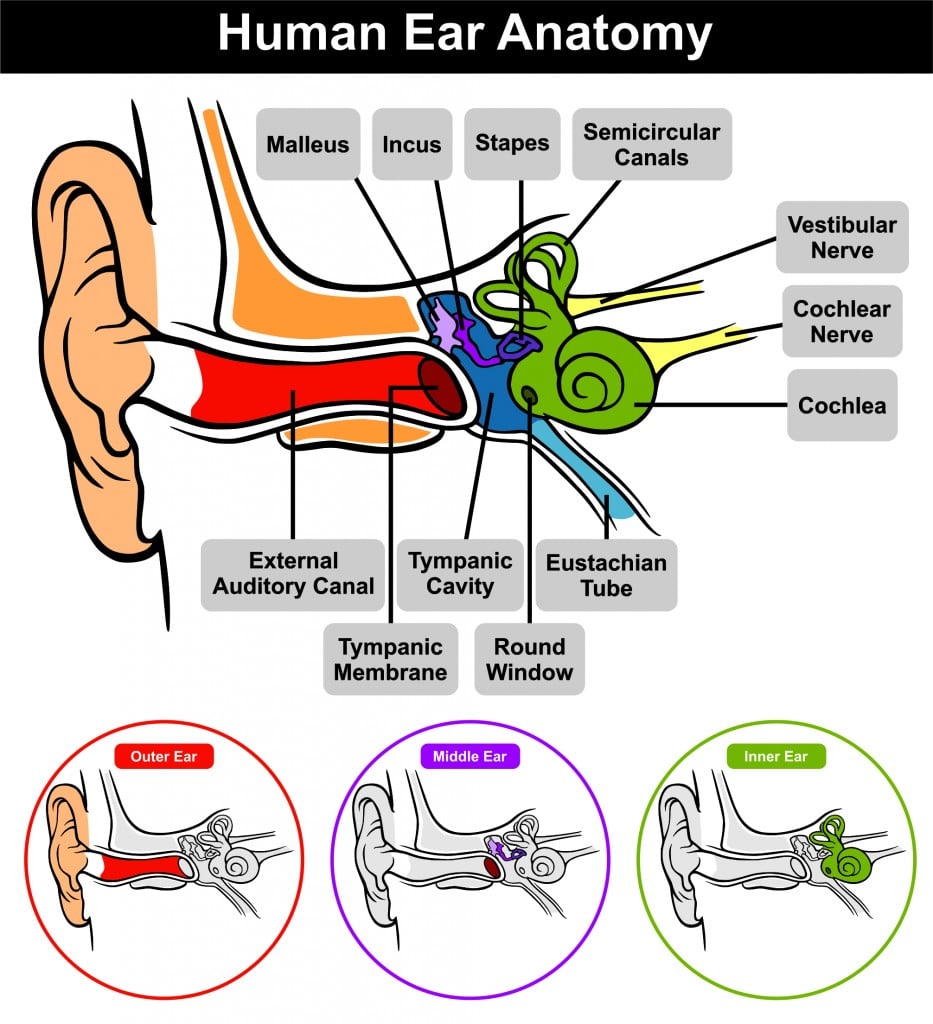
Step-by-step explanation Ear consists of three parts that are outer ear middle ear and inner ear. Static receptors located in the vestibule maculae have otoliths that move when the head moves causing hairs embedded in the otolithic membrane to bend. They change energy from one type to another.
The vestibule is the primary detector of changes in static equilibrium. What are the 2 functional arms of the vestibular apparatus. What is Static Equilibrium.
The receptors are called Ampulla Maculae are the receptors of static equilibrium. Static equilibrium is detected by mechano-receptors found in the vestibule of the inner ear. Describe the different receptors for static and dynamic equilibrium and their locations.
The organ of Corti contains many hair cells present on the basilar membrane which on receiving an auditory signal transmit the signal to the brain by the cochlear nerve. A macula contains numerous receptor cells called hair cells from which numerous stereocilia long microvilli and a single kinocilium a true cilium extend into a glycoprotein gel the otolithic. Static equilibrium is generally easier for.
Dynamic equilibrium is the sense that interprets angular acceleration in the three-axis of rotation which when combined gives a sense of balance when movement is present. Describe the receptors for dynamic and static equilibrium. Hair cells in the cristae of semicircular ducts are used to detect changes involved in maintaining dynamic equilibrium.
Contained in the bony vestibule are two. Dynamic equilibrium is the maintenance of body position in response to movement. What is a static equilibrium.
See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100 2 ratings 3. This gives the idea of a static condition as the name implies. One arm monitors static equilibrium the second arm monitors dynamic equilibrium.
Different frequencies of vibrations stimulate different sets of receptor cells. View ch8docx from ANATOMY 146 at Georgia Northwestern Technical College.

This Image Shows Static Equilibrium The Perception Of Head Orientation By The Macula Dynamic Equilibrium Unli Angular Acceleration Sensory Nerves Chapter 16

Maintaining Static Dynamic Equilibrium How Our Ears Maintain Balance

Module 12 Special Senses Flashcards Quizlet
Maintaining Static Dynamic Equilibrium How Our Ears Maintain Balance

Maintaining Static Dynamic Equilibrium How Our Ears Maintain Balance

Human Ear And Physiology Of Hearing
Maintaining Static Dynamic Equilibrium How Our Ears Maintain Balance

Human Ear And Physiology Of Hearing

Module 12 Special Senses Flashcards Quizlet

Human Ear And Physiology Of Hearing

Special Senses Balance By Amanda Sherry Zack Black Meghan Desai Darin Johnson Mazbura Rahman Ppt Download

Module 12 Special Senses Flashcards Quizlet
Maintaining Static Dynamic Equilibrium How Our Ears Maintain Balance

Module 12 Special Senses Flashcards Quizlet

General Senses Vs Special Senses Google Search Anatomi Undervisning

Human Ear And Physiology Of Hearing

Human Ear And Physiology Of Hearing
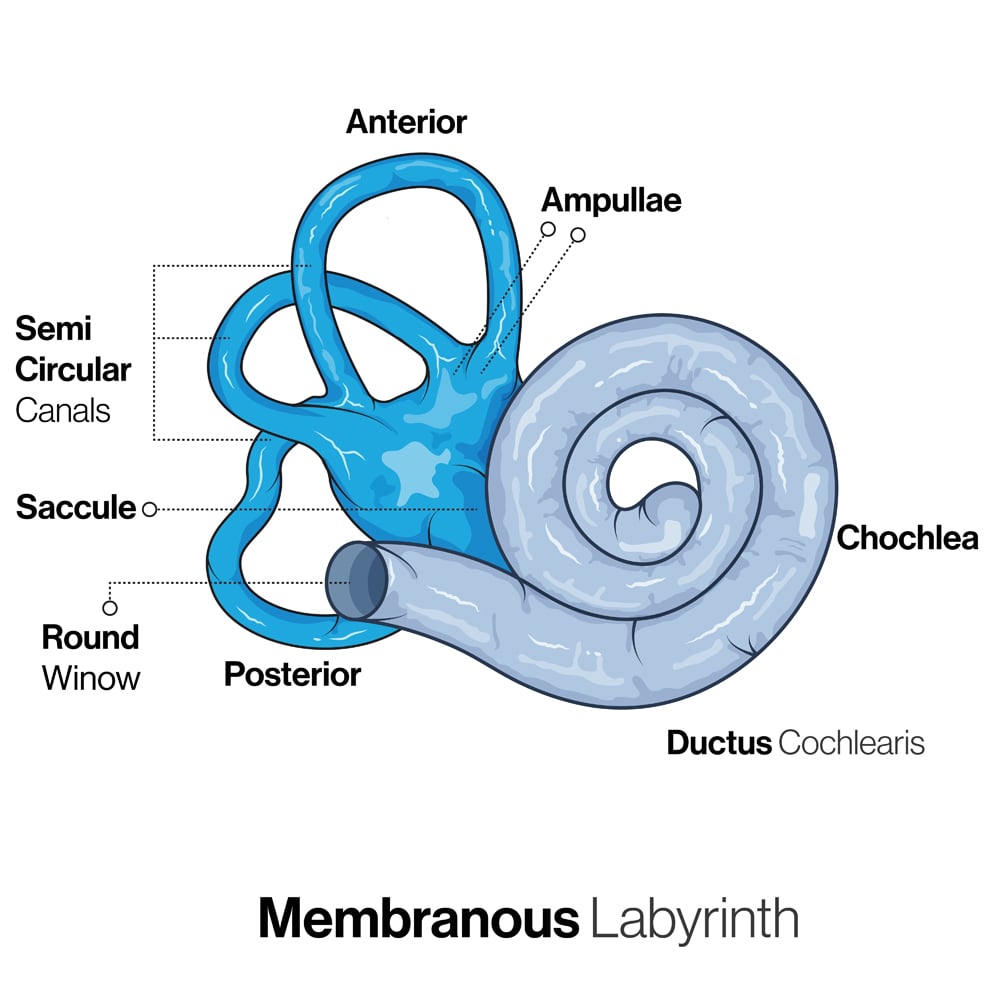
Maintaining Static Dynamic Equilibrium How Our Ears Maintain Balance

Comments
Post a Comment