Describe the Structure of Red Blood Cells
Neutrophils and monocytes are phagocytic cells that are part of the innate and also the adaptive immune response. In mammals red blood cells are small biconcave cells that at maturity do not contain a nucleus or mitochondria and are only 78 µm in size.
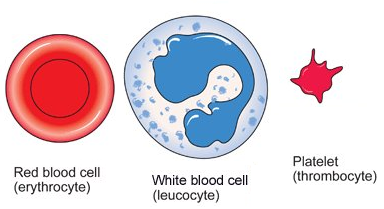
Blood Cells Structure And Functions Biology Notes For Igcse 2014
The RBC membrane hemoglobin structure and function metabolic pathways.
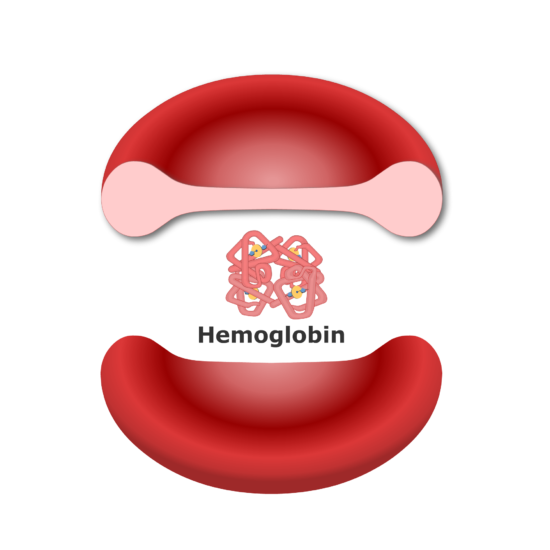
. First week only 499. The need to deform and squeeze through. A red blood cell is sometimes simply referred to as a red cell.
The shape can vary drastically with many different forms of red blood cells described in the literature. List the two most important red blood cell RBC. Plasma is lighter so it floats on the top.
Cyte cell are specialized cells that circulate through the body delivering oxygen to cells. It is also called an erythrocyte or rarely today a red blood corpuscle. Red blood cells contain numerous hemoglobin molecules resulting in their sickle-shaped appearance.
The most important part of a red blood cell is hemoglobin which is essentially the functional component of the cell. Start your trial now. Normal red blood cell counts differ based on the individual.
Red blood cells contain oxygen in their outer perimeter and none within the center resulting in their flattened disc-like shape. They have no nucleus so they can contain more haemoglobin. As they mature RBCs extrude their nucleus and fill their cytoplasm with hemoglobin Hb molecules which bind and transport oxygen O2 and carbon dioxide CO2.
47 to 61 million red blood cells per microliter of blood. Their relative amounts can be measured by the packed volume after the centrifugation. During this process stem cell derived erythroid precursors undergo a series of morphological changes to become.
Red blood cells RBCs are circular biconcave disc-shaped cells containing pigments like hemoglobin in order to transport mainly oxygen throughout the body of animals. Solution for Describe the structure of a red blood cell and hemoglobin. Start your trial now.
Describe the structure function and production of red blood cells. Red cells have a major function in transport of oxygen and minor functions in regulation of local blood flow and transport of carbon dioxide. Red blood cells and white blood cells are the two components of blood in animals.
The major function of red cells is the uptake of oxygen from the lungs and its delivery to the tissues by oxygenation of the ferrous Fe ions of haem. It appears dumbbell-shaped in profile. Red blood cells are the main type of blood cell in the blood plasma they are also called erythrocytes and have oxygen carrying properties.
Carbon dioxide nucleus Mature The shape of the cell allows oxygen exchange at a constant rate over the largest possible area low cellular hemoglobin convex The red blood cell is further adapted by lacking a Since possessing the following organelle requires large amounts of. Around 98 of oxygen transport is by red cells only 2 being transported in the plasma. The diameter of a red blood cell.
They cannot independently synthesize proteins. Red blood cells contain numerous nuclei and are often filled with oxygen resulting in a round donut shape. They pick up oxygen and release carbon dioxide at the lungs where the capillaries and alveolis are in very close contact the carbon dioxide diffuses from the capillary membrane into the alveoli membrane while the oxygen diffuses in.
However enzymes within the red blood cells allow it to produce small amounts of energy ATP from glucose. Eosinophils have their major function in protecting against multicellular parasites and basophils participate in this. Red blood cells or erythrocytes erythro red.
Red blood cells are considered cells but they lack a nucleus DNA and organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria. Red blood cells are denser so they are span down to the bottom. Here the four hemes attach to a single protein to form a polypeptide chain.
They are small and flexible so that they can fit through narrow blood vessels. 42 to 54 million red blood cells per microliter of blood. RBCs are small disc-shaped cells that measure 7 8 micrometers μm in diameter.
First week only 499. The mature human red blood cell is small round and biconcave. Red blood cells cannot divide or replicate like other bodily cells.
The red cell has a diameter greater than that of a capillary. Explain why exercising at high altitudes injecting synthetic EPO and blood doping increase red blood cell concentrations 14. Unlike the other cells in the body red blood cells are made up of pigments known and hemoglobin composed of 4 hemes which gives erythrocytes the red color and a globin protein.
They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow. Red blood cell agglutination means that the cells are clumped together in a cluster and rouleaux refers to the erythrocytes arranged in a linear formation. Erythrocytes red blood cells or RBCs are anucleate biconcave cells filled with hemoglobin that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and tissues.
They are adapted to be round and flexible so it may pass through extremely small blood vessels. 40 to 55 million red blood cells per microliter of blood. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments.
Describe the process of blood clotting 15. The chemical composition of the membrane mass is approximately 40 lipids 52 proteins and 8 carbohydrates. Describe the chemical composition of the red cell membrane in terms of percentage of lipids proteins and carbohydrates.
Solution for Describe the structure and function of red blood cells white blood cells and platelets. They are produced in the red bone marrow by a process called erythropoiesis. The bloods red color is due to the spectral properties of the hemic iron ions in hemoglobin.
It lacks a nucleus mitochondria or endoplasmic reticulum. Red blood cells have an unusual structure compared to other cells in the human body. Weve got the study and writing resources you need for your assignments.
They have a biconcave shape flattened disc shape to. Healthy Red Blood Cell Structure The discocyte shape of human RBCs is approximately 75 to 87 μm in diameter and 17 to 22 μm in thickness Figure 1. Hemoglobin molecules essential for gas transport within the circulation are contained in the RBC cytosol.
Between the plasma and RBCs is a thin layer of the white stuff called Buffy coat.
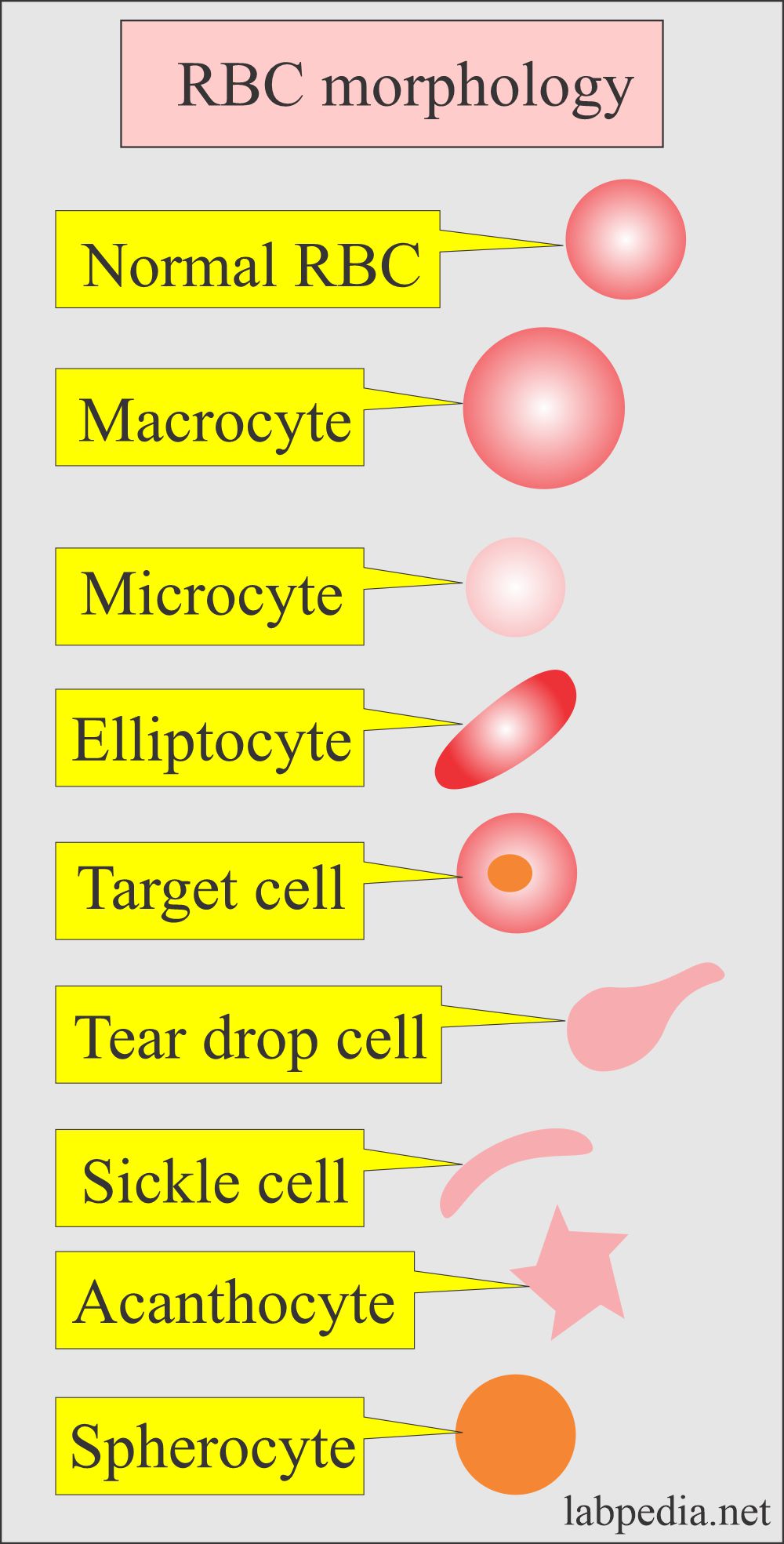
Complete Blood Count Red Blood Cell Morphology

Hemoglobin Molecule Structure Function
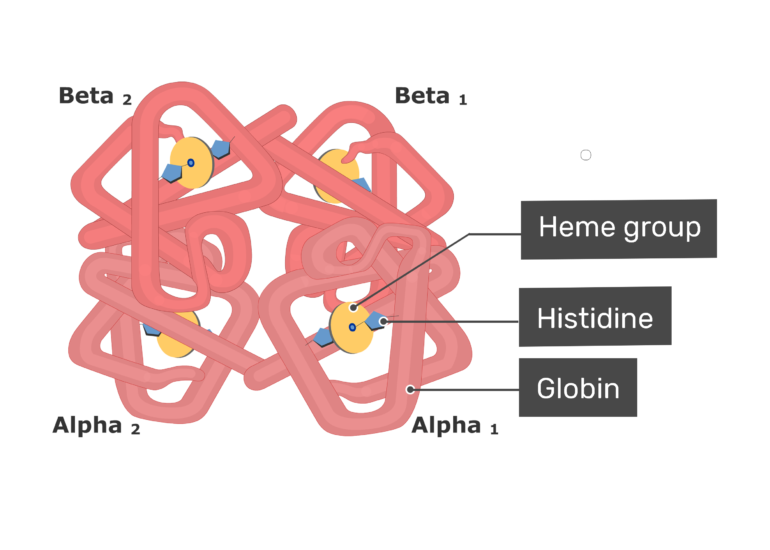
Hemoglobin Molecule Structure Function
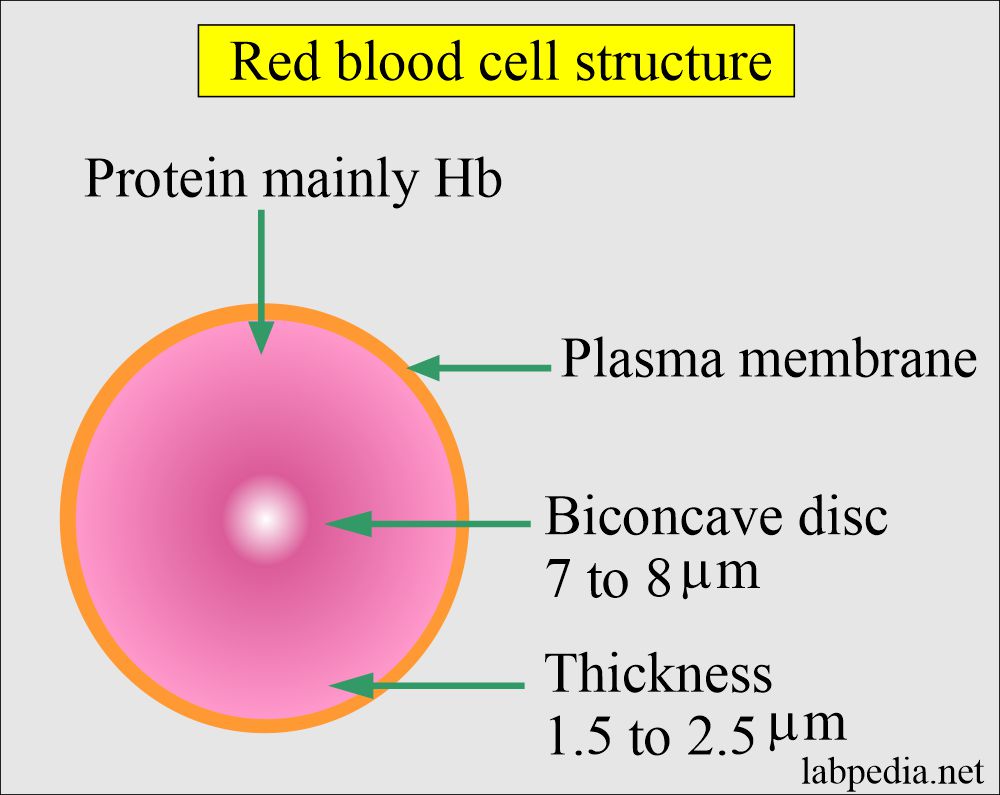
Complete Blood Count Red Blood Cell Morphology
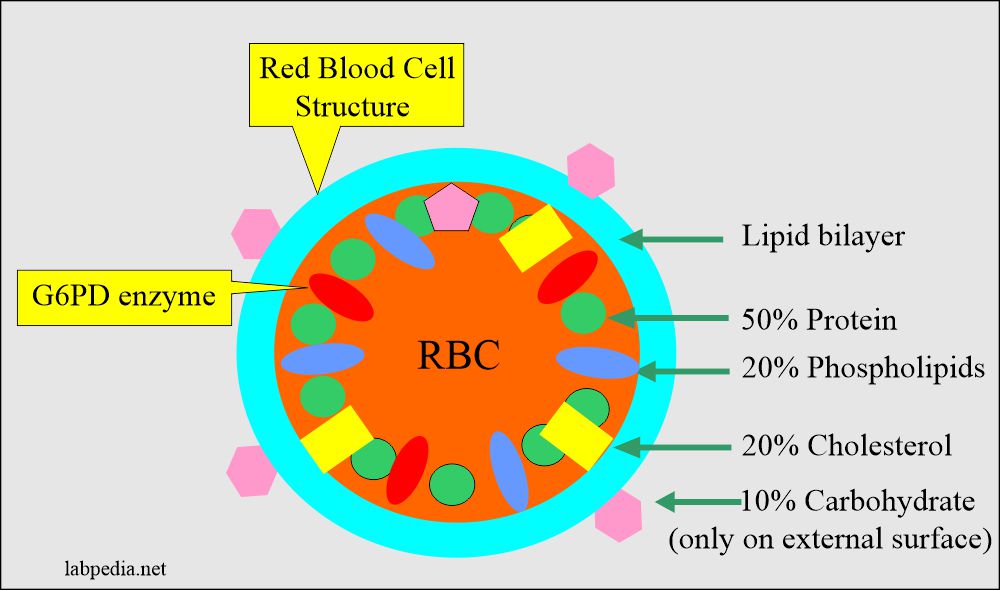
Complete Blood Count Red Blood Cell Morphology

Lesson Explainer Components Of The Blood Nagwa
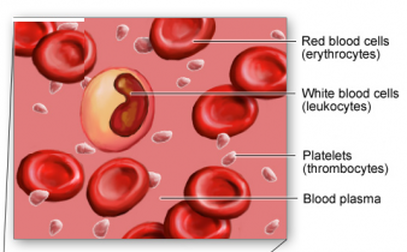
Blood Cells Structure And Functions Biology Notes For Igcse 2014
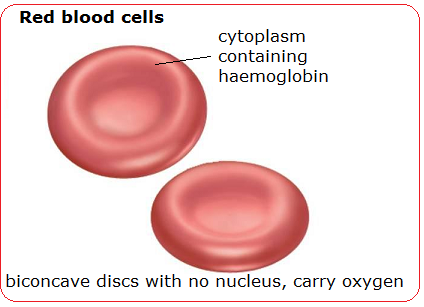
Blood Cells Structure And Functions Biology Notes For Igcse 2014
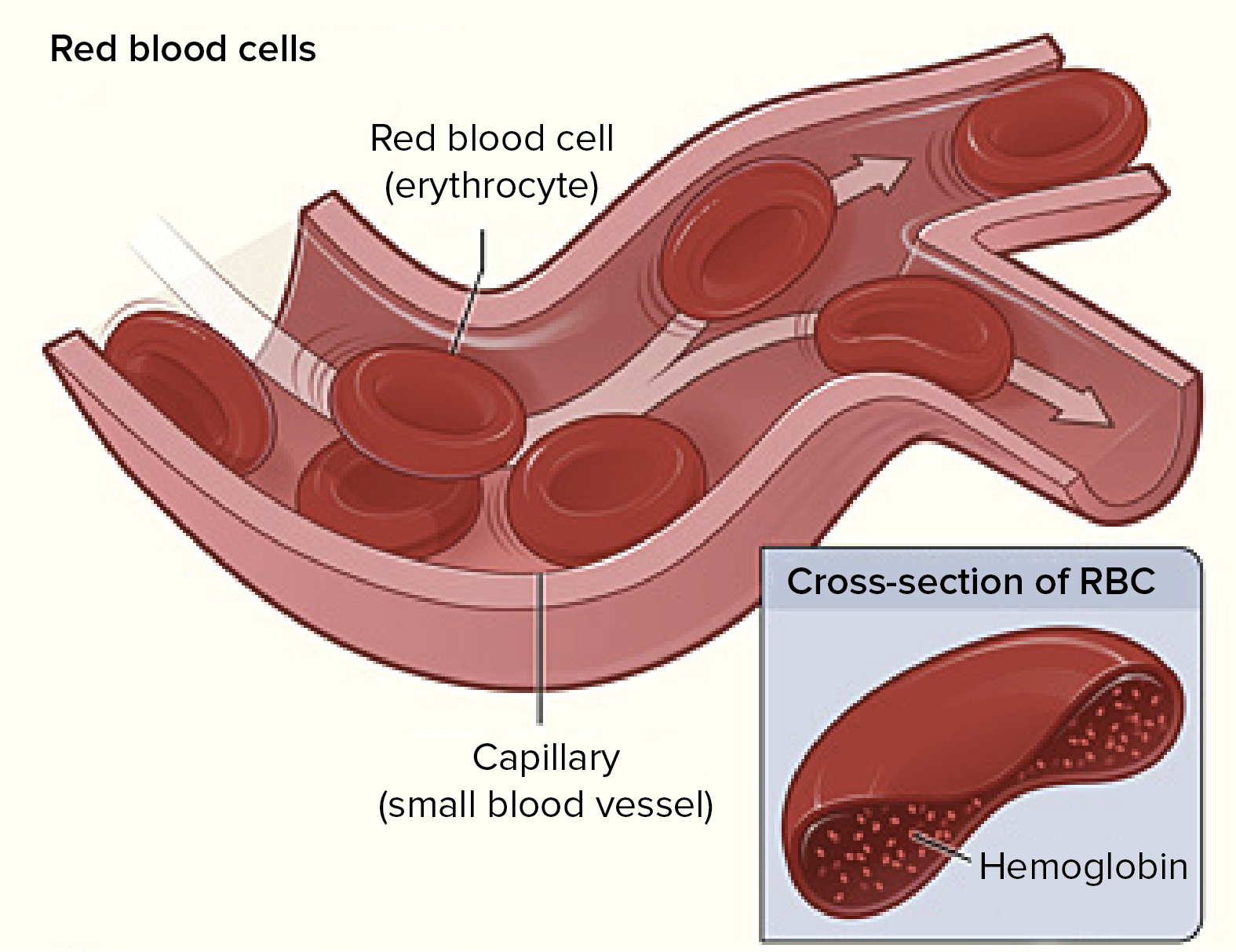
Components Of Blood Article Khan Academy
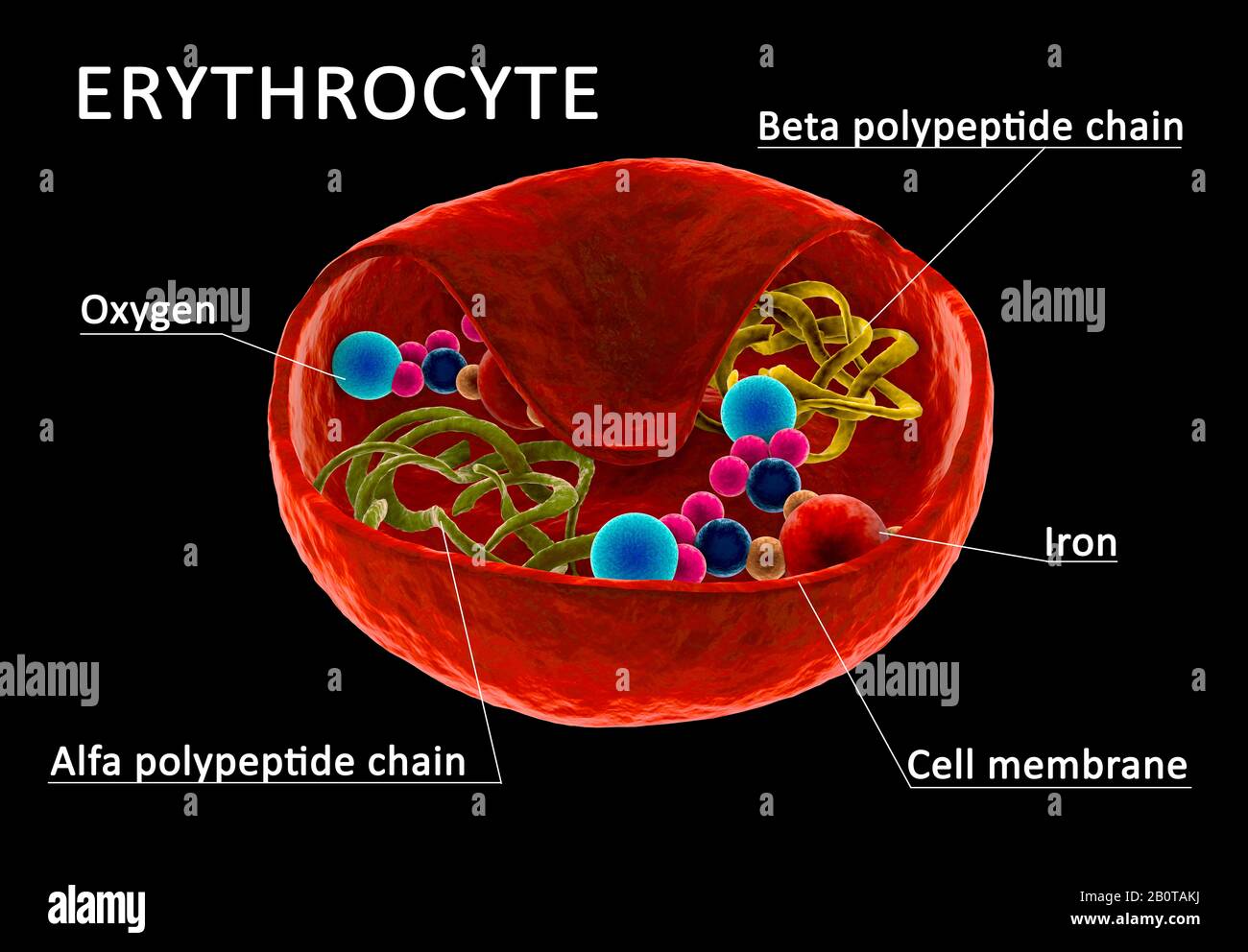
Structure Of Red Blood Cell Erythrocyte With Visible Hemoglobine And Polypetide Chain Section Through Cell Membrane 3d Illustration Stock Photo Alamy

Structure Of The Red Blood Cell Erythrocyte Vector Image
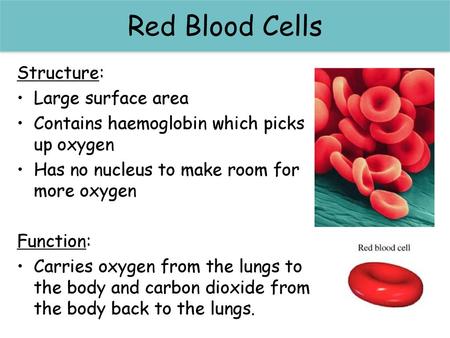
Red Blood Cells Red Blood Cells Structure Large Surface Area Ppt Video Online Download
What Is The Function Of Hemoglobin In The Human Body Pediaa Com
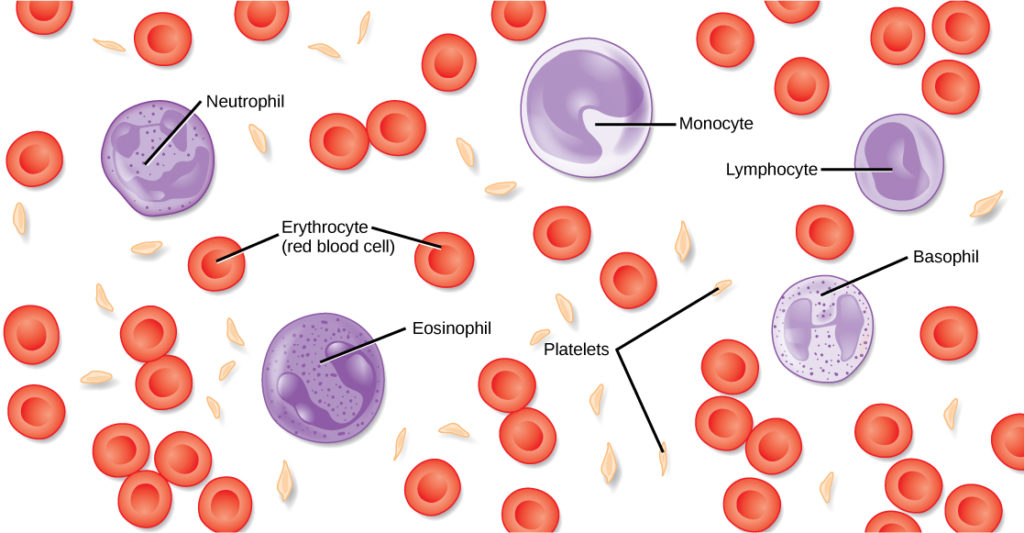
Structure And Function Of Blood Biology For Majors Ii
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12313/Erythrocytes.png)
Erythrocytes Histology Structure Function Life Cycle Kenhub
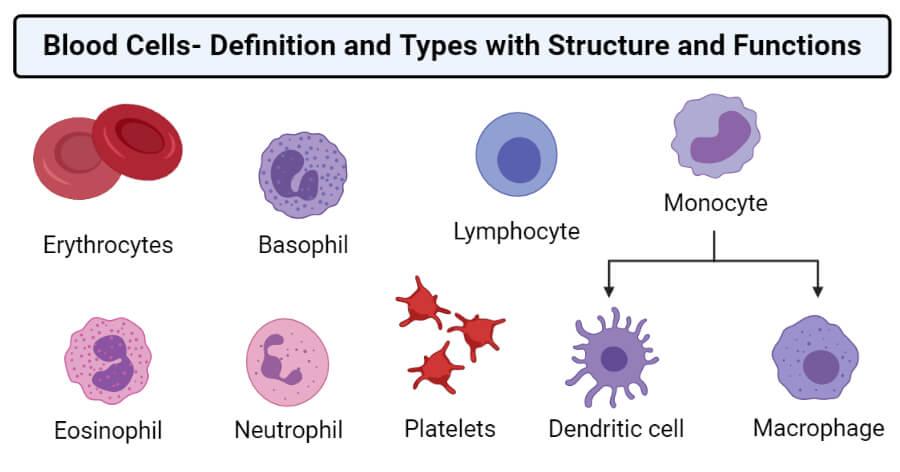
Blood Cells Definition And Types With Structure And Functions
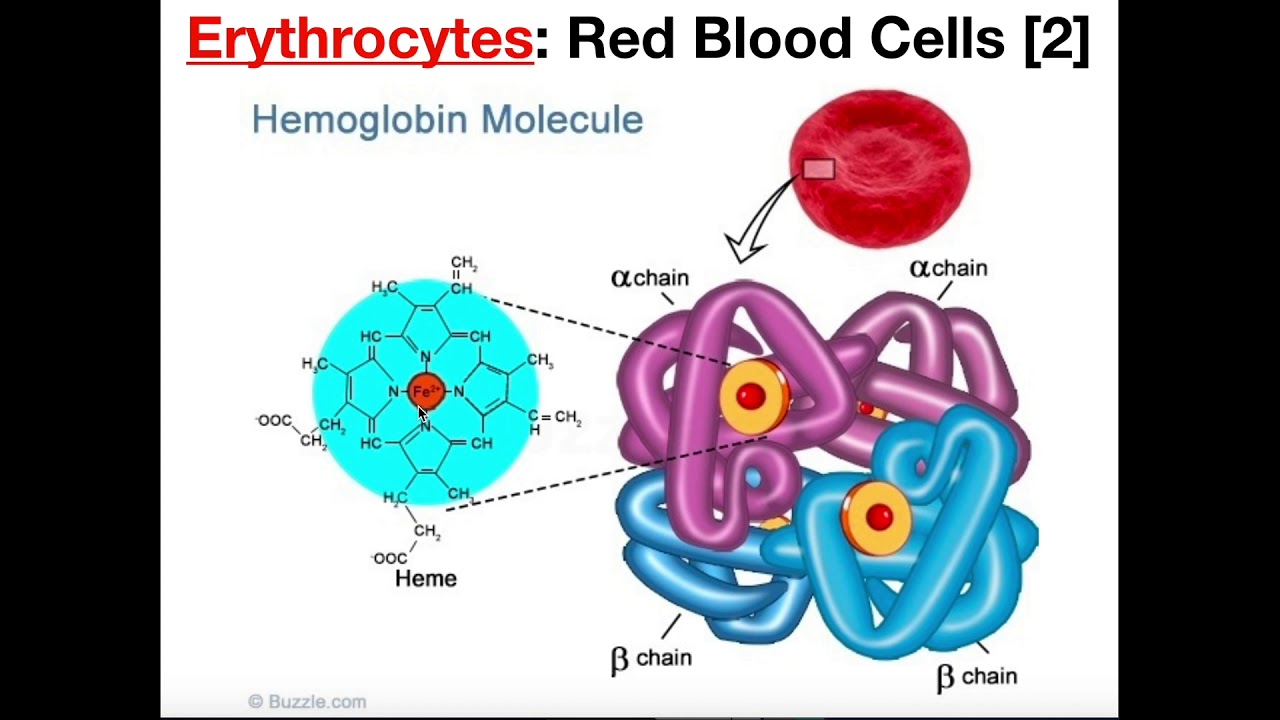
Structure And Function Of Erythrocytes Rbcs Youtube
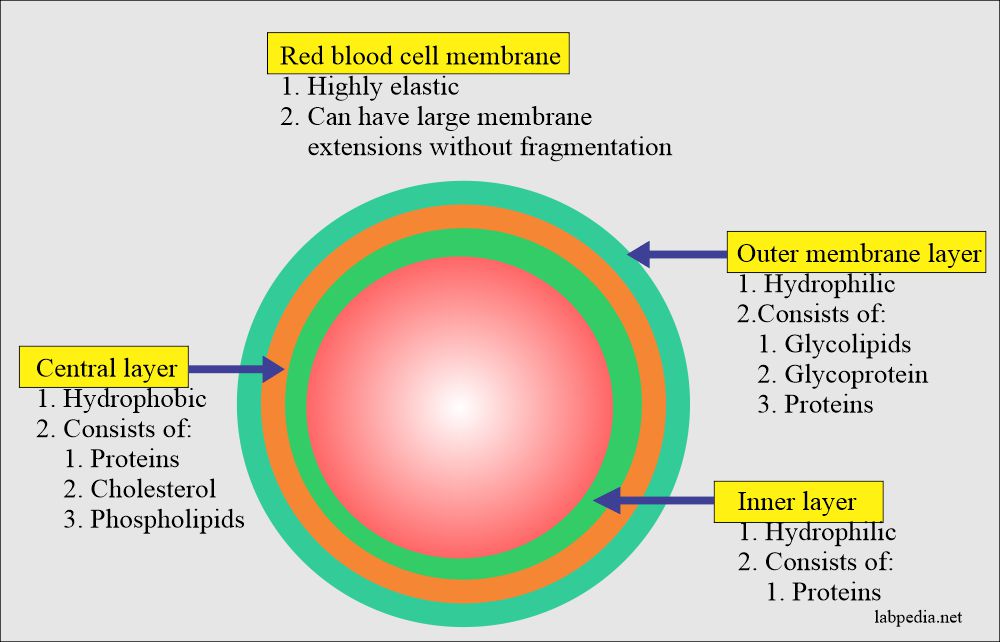
Complete Blood Count Red Blood Cell Morphology
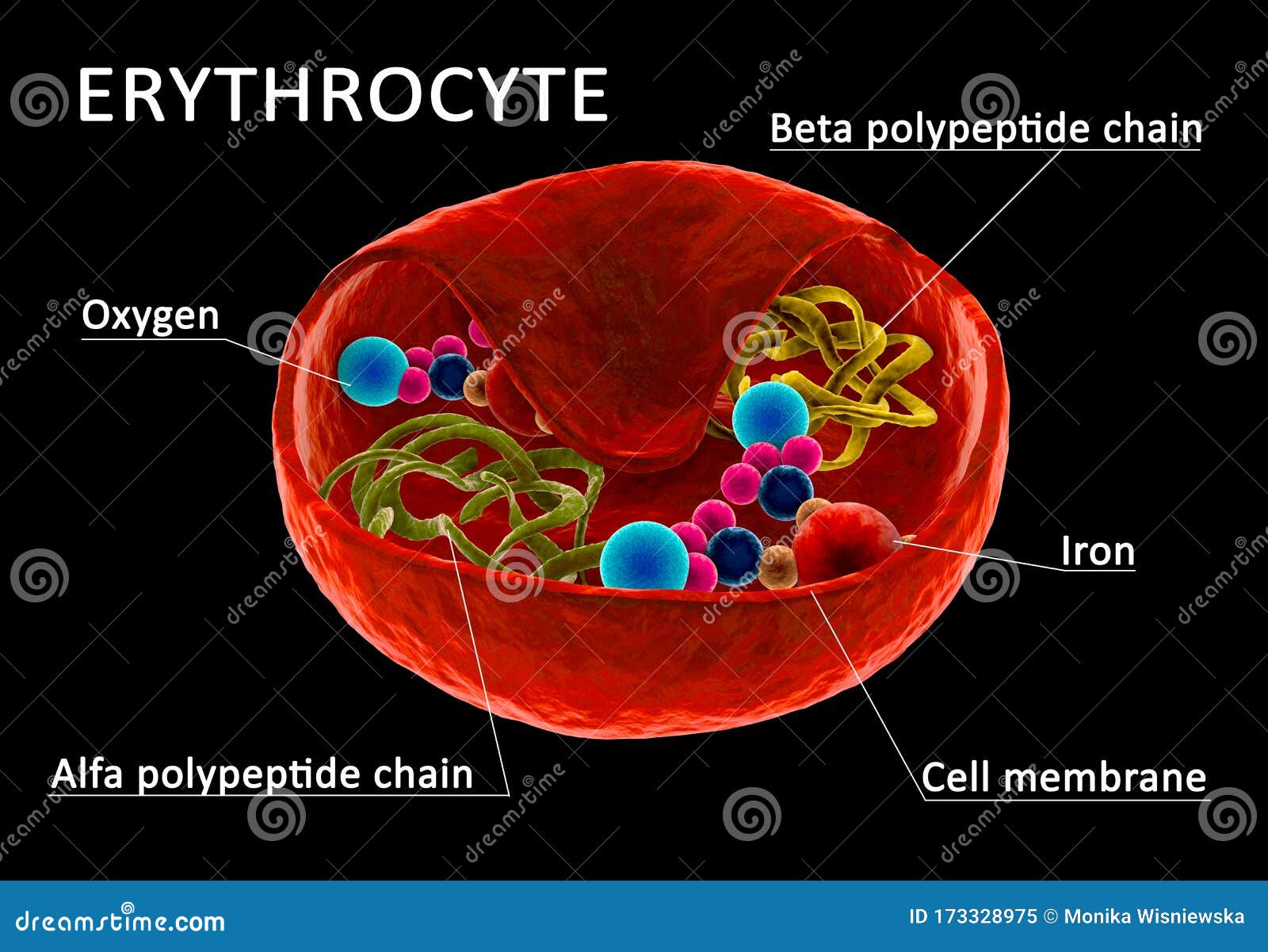
Red Blood Cell Structure Stock Illustration Illustration Of Capillary 173328975
Comments
Post a Comment